Usage Guide
This guide covers the complete setup and usage of the Online Feature Store system, including the core services (Online Feature Store and Horizon) and the TruffleBox UI for feature management.
Table of Contents
System Overview
The Online Feature Store is a comprehensive feature management system consisting of two main components:
- Online Feature Store: The core feature serving service that provides real-time feature retrieval with multiple storage backends and caching layers
- Horizon: The configuration and metadata management service that handles feature definitions, stores, and job configurations
These services work together to provide a scalable, high-performance feature store for machine learning applications.
Environment Setup
Online Feature Store Configuration
The Online Feature Store requires several environment variables to configure storage backends, caching, and service settings.
Core Application Settings
APP_ENV=prod
APP_LOG_LEVEL=DEBUG
APP_METRIC_SAMPLING_RATE=1
APP_NAME=online-feature-store
APP_PORT=8005
AUTH_TOKEN=ofs-token
Storage Configuration
ScyllaDB Storage (Primary Storage)
# Primary ScyllaDB cluster
STORAGE_SCYLLA_1_CONTACT_POINTS=localhost
STORAGE_SCYLLA_1_KEYSPACE=ofs
STORAGE_SCYLLA_1_NUM_CONNS=1
STORAGE_SCYLLA_1_PORT=9042
STORAGE_SCYLLA_1_TIMEOUT_IN_MS=300000
STORAGE_SCYLLA_1_PASSWORD=
STORAGE_SCYLLA_1_USERNAME=ofs
# Secondary ScyllaDB cluster
STORAGE_SCYLLA_5_CONTACT_POINTS=localhost
STORAGE_SCYLLA_5_KEYSPACE=onfs
STORAGE_SCYLLA_5_NUM_CONNS=1
STORAGE_SCYLLA_5_PASSWORD=
STORAGE_SCYLLA_5_PORT=9042
STORAGE_SCYLLA_5_TIMEOUT_IN_MS=300000
STORAGE_SCYLLA_5_USERNAME=
# Active ScyllaDB configurations
STORAGE_SCYLLA_ACTIVE_CONFIG_IDS=1,5
Redis Storage Configuration
Redis serves dual purposes in the Online Feature Store:
- Primary Storage Backend: For fast feature retrieval and storage
- Distributed Cache Layer: For improved performance and reduced latency
Redis configurations can be referenced by their IDs in Store configurations, similar to ScyllaDB. Each Redis configuration can be independently used as either a storage backend or cache layer.
# Redis Failover Configuration 1 (ID: 2)
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_2_SENTINEL_ADDRESSES=localhost:26379
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_2_DB=0
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_2_DISABLE_IDENTITY=true
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_2_MASTER_NAME=mymaster
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_2_MAX_IDLE_CONN=32
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_2_MIN_IDLE_CONN=20
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_2_MAX_ACTIVE_CONN=32
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_2_MAX_RETRY=-1
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_2_POOL_FIFO=false
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_2_READ_TIMEOUT_IN_MS=3000
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_2_WRITE_TIMEOUT_IN_MS=3000
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_2_POOL_TIMEOUT_IN_MS=3000
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_2_POOL_SIZE=32
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_2_CONN_MAX_IDLE_TIMEOUT_IN_MINUTES=15
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_2_CONN_MAX_AGE_IN_MINUTES=30
# Redis Failover Configuration 2 (ID: 4)
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_4_SENTINEL_ADDRESSES=localhost:26379
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_4_DB=0
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_4_DISABLE_IDENTITY=true
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_4_MASTER_NAME=mymaster
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_4_MAX_IDLE_CONN=32
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_4_MIN_IDLE_CONN=20
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_4_MAX_ACTIVE_CONN=32
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_4_MAX_RETRY=-1
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_4_POOL_FIFO=false
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_4_READ_TIMEOUT_IN_MS=3000
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_4_WRITE_TIMEOUT_IN_MS=3000
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_4_POOL_TIMEOUT_IN_MS=3000
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_4_POOL_SIZE=32
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_4_CONN_MAX_IDLE_TIMEOUT_IN_MINUTES=15
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_4_CONN_MAX_AGE_IN_MINUTES=30
# High-Performance Redis Configuration (ID: 6)
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_6_CONN_MAX_AGE_IN_MINUTES=-1
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_6_CONN_MAX_IDLE_TIMEOUT_IN_MINUTES=30
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_6_DB=0
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_6_DISABLE_IDENTITY=true
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_6_MASTER_NAME=mymaster
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_6_MAX_ACTIVE_CONN=202
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_6_MAX_IDLE_CONN=157
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_6_MAX_RETRY=-1
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_6_MIN_IDLE_CONN=52
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_6_PASSWORD=
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_6_POOL_FIFO=false
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_6_POOL_SIZE=202
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_6_POOL_TIMEOUT_IN_MS=2
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_6_READ_TIMEOUT_IN_MS=75
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_6_ROUTE_RANDOM=true
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_6_SENTINEL_ADDRESSES=localhost:26379
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_6_WRITE_TIMEOUT_IN_MS=300
# Active Redis configurations
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_ACTIVE_CONFIG_IDS=2,4,6
Caching Configuration
# In-Memory Cache
IN_MEM_CACHE_3_ENABLED=true
IN_MEM_CACHE_3_NAME=onfs
IN_MEM_CACHE_3_SIZE_IN_BYTES=10000000
IN_MEM_CACHE_ACTIVE_CONFIG_IDS=3
# Distributed Cache (uses Redis configurations)
# Redis configurations (IDs: 2,4,6) can be used for distributed caching
DISTRIBUTED_CACHE_CONF_IDS=2
Service Discovery and Configuration
# ETCD Configuration for service discovery
ETCD_SERVER=0.0.0.0:2379
ETCD_WATCHER_ENABLED=true
Horizon Configuration
Horizon manages the metadata and configuration for the Online Feature Store system.
Core Application Settings
APP_NAME=horizon
APP_ENVIRONMENT=PROD
APP_ENV=production
APP_PORT=8082
APP_LOG_LEVEL=DEBUG
APP_METRIC_SAMPLING_RATE=1
APP_GC_PERCENTAGE=1
Database Configuration
# MySQL Master Configuration
MYSQL_MASTER_MAX_POOL_SIZE=5
MYSQL_MASTER_MIN_POOL_SIZE=2
MYSQL_MASTER_PASSWORD=
MYSQL_MASTER_HOST=127.0.0.1
MYSQL_MASTER_PORT=3306
MYSQL_DB_NAME=ml_config
MYSQL_MASTER_USERNAME=root
# MySQL Slave Configuration
MYSQL_SLAVE_MAX_POOL_SIZE=5
MYSQL_SLAVE_MIN_POOL_SIZE=2
MYSQL_SLAVE_PASSWORD=
MYSQL_SLAVE_HOST=127.0.0.1
MYSQL_SLAVE_USERNAME=root
MYSQL_SLAVE_PORT=3306
ScyllaDB Configuration
# ScyllaDB for Horizon
SCYLLA_1_CONTACT_POINTS=localhost
SCYLLA_1_KEYSPACE=onfs
SCYLLA_1_NUM_CONNS=1
SCYLLA_1_PORT=9042
SCYLLA_1_TIMEOUT_IN_MS=300000
SCYLLA_1_PASSWORD=
SCYLLA_1_USERNAME=
SCYLLA_ACTIVE_CONFIG_IDS=1
Service Integration
# ETCD Configuration
ETCD_WATCHER_ENABLED=true
ETCD_SERVER=localhost:2379
# Integration with Online Feature Store
ONLINE_FEATURE_STORE_APP_NAME=online-feature-store
Key Constructs
Understanding these key constructs is essential for effectively using the Online Feature Store:
Store ID
A Store ID is a unique identifier that represents a data storage configuration within the system. It defines:
- Storage Backend: Which underlying storage system (ScyllaDB, Redis, etc.) to use
- Configuration Parameters: Connection settings, timeouts, pool sizes
- Access Patterns: How data is read from and written to the store
Store IDs are referenced throughout the system to:
- Route feature requests to the appropriate storage backend
- Apply specific caching strategies
- Manage data lifecycle and retention policies
- Configure stores in TruffleBox UI for feature groups and entities
Storage Backend Configuration:
- ScyllaDB Store IDs:
STORAGE_SCYLLA_ACTIVE_CONFIG_IDS=1,5indicates ScyllaDB configurations with IDs 1 and 5 are active - Redis Store IDs:
STORAGE_REDIS_FAILOVER_ACTIVE_CONFIG_IDS=2,4,6indicates Redis configurations with IDs 2, 4, and 6 are active
Dual Usage of Redis: Redis configurations can serve dual purposes:
- As Storage Backend: Redis IDs (2,4,6) can be configured as primary storage in Store configurations
- As Distributed Cache: Same Redis IDs can be used for caching via
DISTRIBUTED_CACHE_CONF_IDS=2
When creating stores in TruffleBox, you can reference these storage configuration IDs to determine which backend (ScyllaDB ID 1/5 or Redis ID 2/4/6) will be used for your feature data.
Entity
An Entity represents a logical grouping of related features, typically corresponding to a business object (e.g., User, Product, Transaction). Entities provide:
- Namespace: Logical separation of feature groups
- Identity: Primary key definition for feature lookup
- Configuration: Cache settings and storage preferences
Feature Group
A Feature Group is a collection of related features that share:
- Common Entity: All features belong to the same entity
- Storage Configuration: Same underlying storage and caching strategy
- Data Lifecycle: Shared TTL and retention policies
- Access Patterns: Similar read/write characteristics
Feature
A Feature is an individual data point that can be retrieved for machine learning models. Each feature has:
- Name: Unique identifier within its feature group
- Data Type: The type of data stored (string, integer, float, etc.)
- Default Value: Value returned when feature data is not available
- Source Mapping: How the feature maps to underlying storage columns
Job
A Job represents a data processing pipeline that:
- Ingests Data: Processes raw data from various sources
- Transforms Features: Applies business logic and computations
- Updates Storage: Writes processed features to the feature store
- Scheduling: Defines when and how often the job runs
Configuration Hierarchy
The system uses a hierarchical configuration approach:
Store → Entity → Feature Group → Feature
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
Config Identity Collection Individual
Level Level Level Level
This hierarchy allows for:
- Inheritance: Lower levels inherit settings from higher levels
- Override: Specific configurations can be overridden at each level
- Flexibility: Different storage strategies for different use cases
TruffleBox UI Guide
TruffleBox is a comprehensive and intuitive UI to help users onboard new features, models and related entities easily. We will build iteratively and add support overtime for entire feature lifecycle management.
Table of Contents
User Flow
Getting Started with TruffleBox
Authentication
Users can access TruffleBox through registration or login:
Registration:
- New users should fill in all details and click Register.
- Once Registered, Please wait for an admin to activate your User
User Management
Admin users can manage other users through the User Management interface:
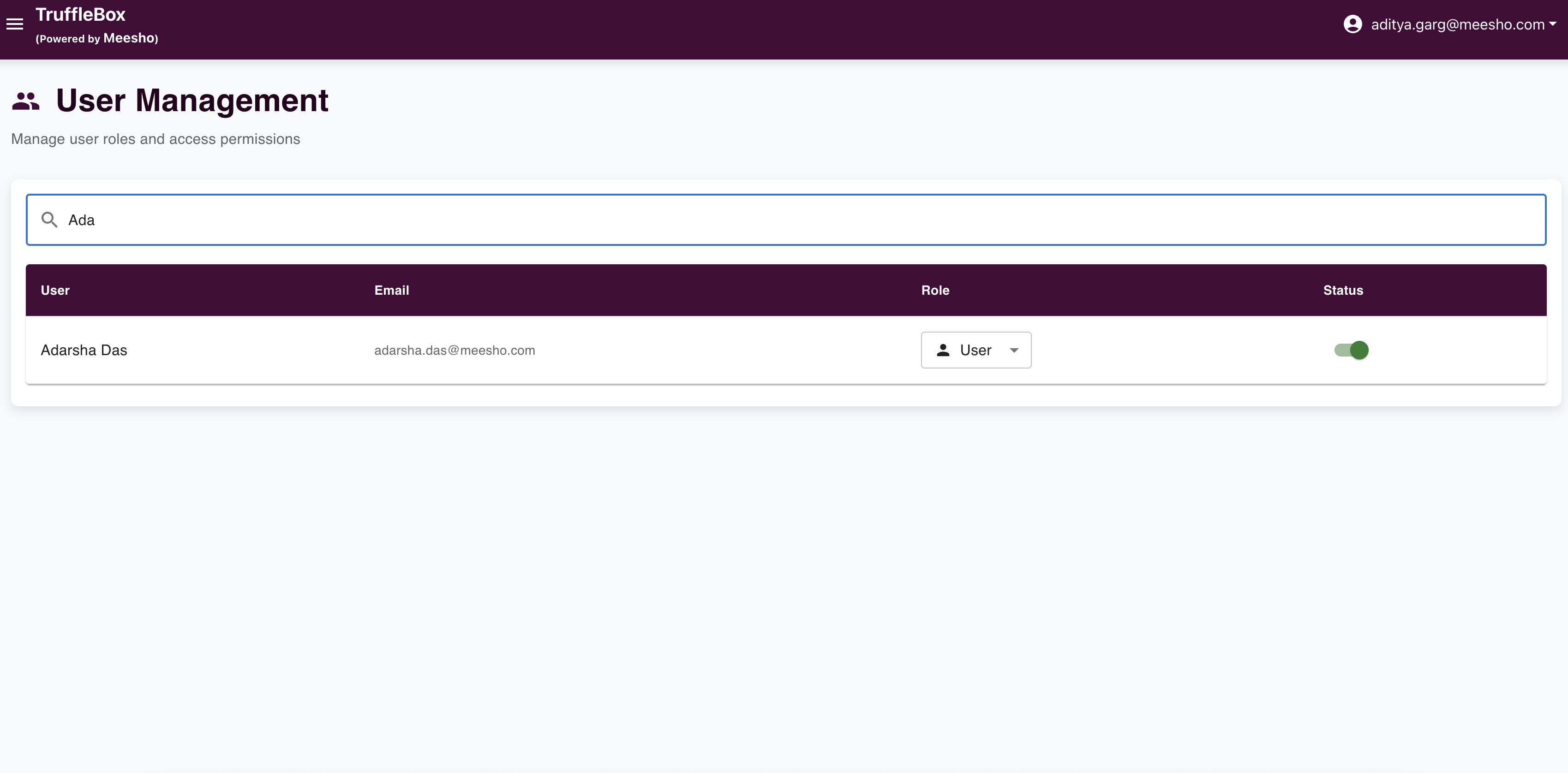
In the User Management page, admins can:
- View all registered users
- Activate/deactivate user accounts
- Modify user roles
- Manage user permissions
This is a crucial step in the user onboarding process as new users must be activated by an admin before they can log in to the system.
Login: Existing users can login with their registered email and password.
Navigation
After logging in, you'll be redirected to the feature-discovery page. Access the Control Center by clicking the hamburger icon in the top left corner.

Feature Discovery
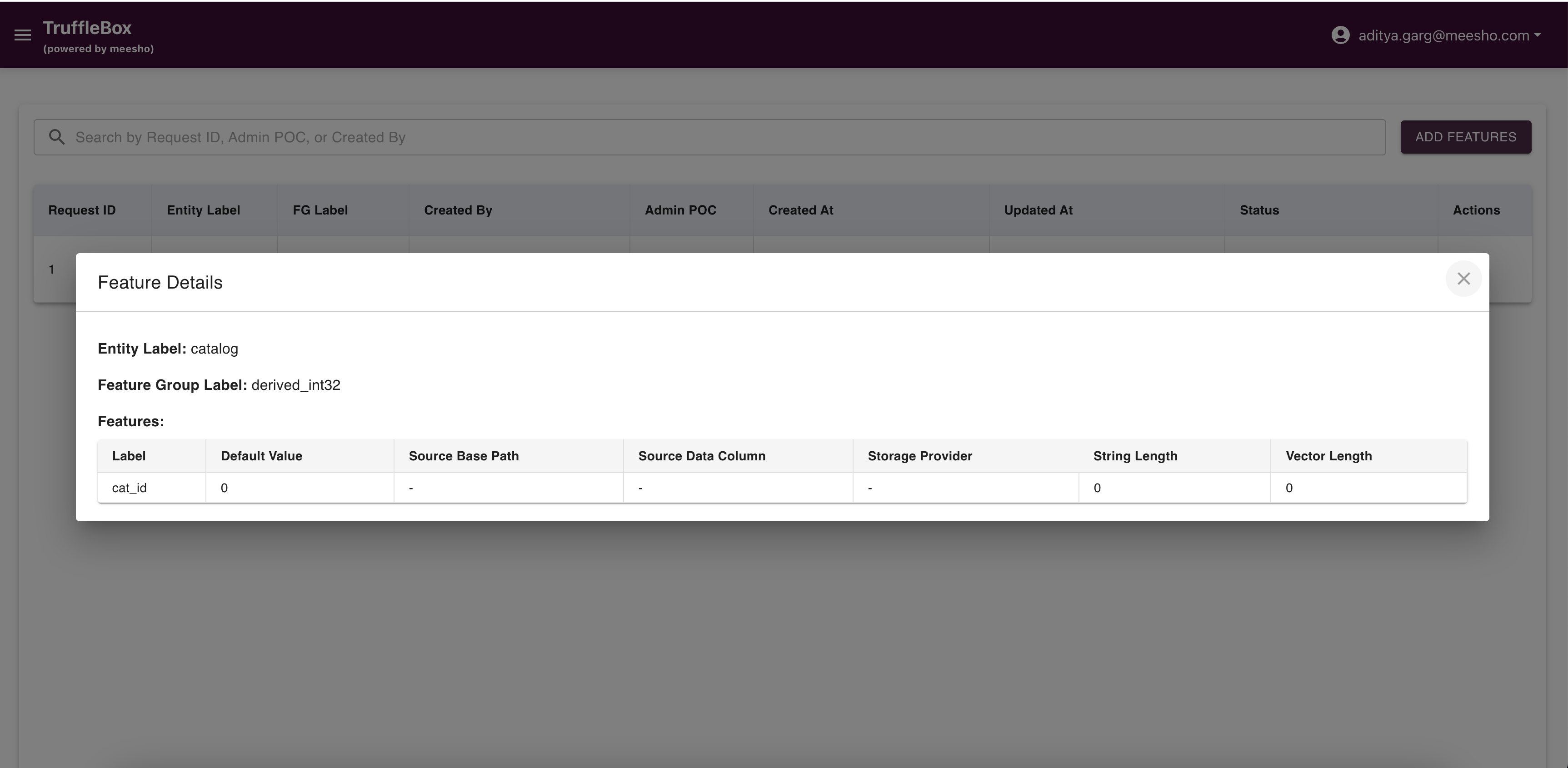
The Feature Discovery page displays approved entities, feature groups, and features.
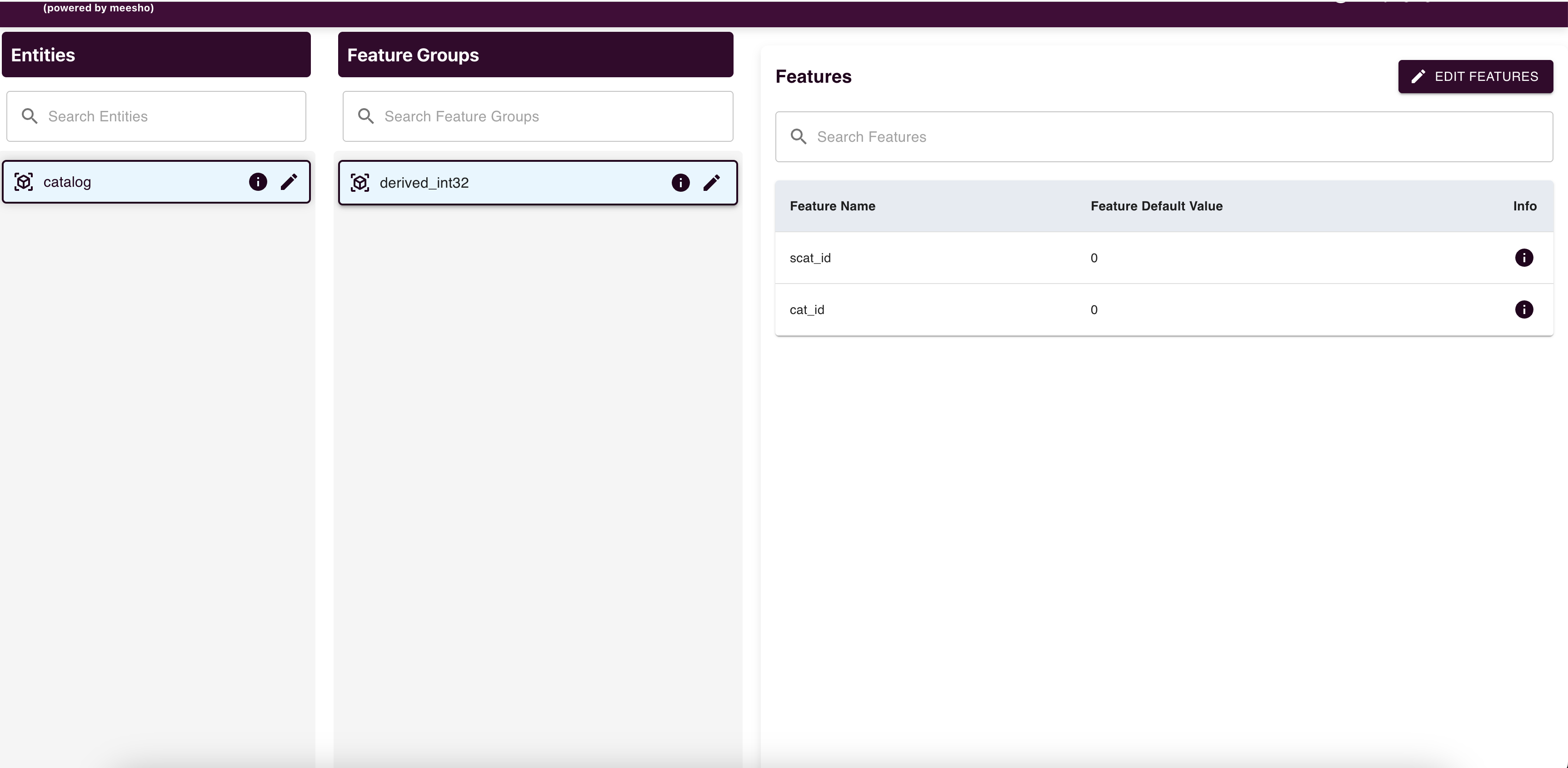
You can:
- View details by clicking the info icon
- Edit entities, feature groups, and features as needed
Entity Management
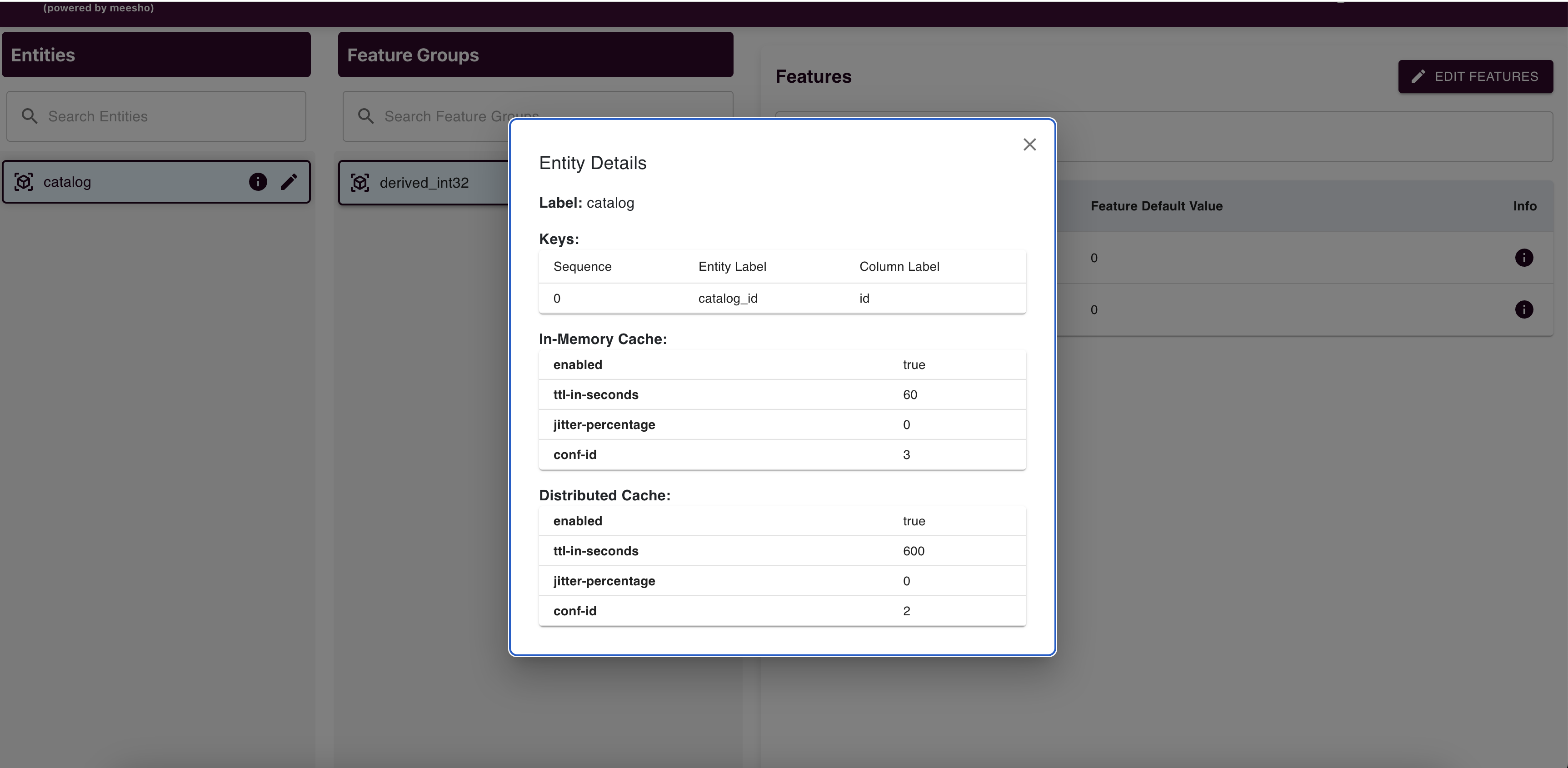
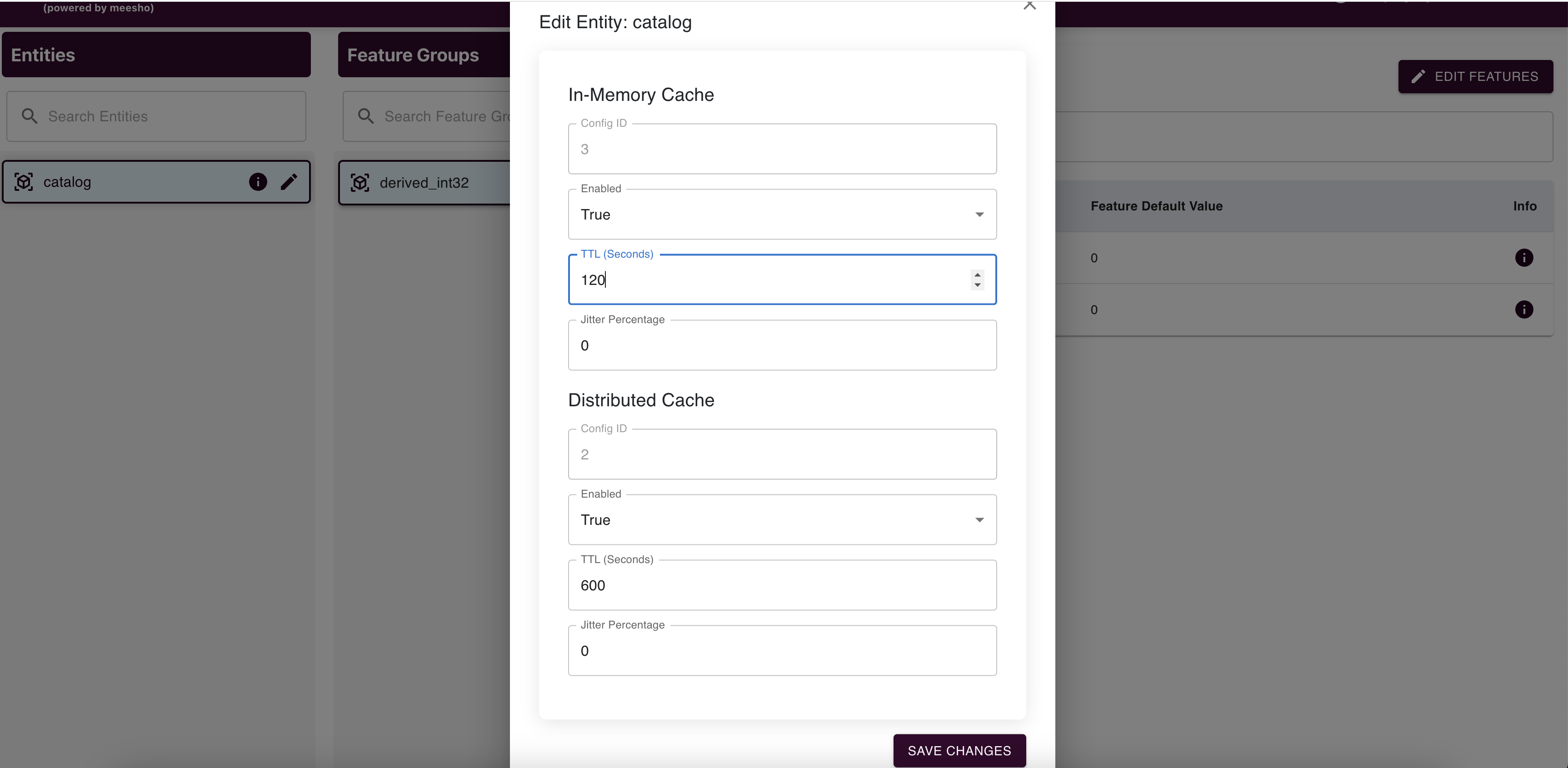
View entity details and edit them (limited to In Memory Cache and Distributed Cache details excluding config ID). Submit changes via "Save Changes" to raise an edit request.
Feature Group Management
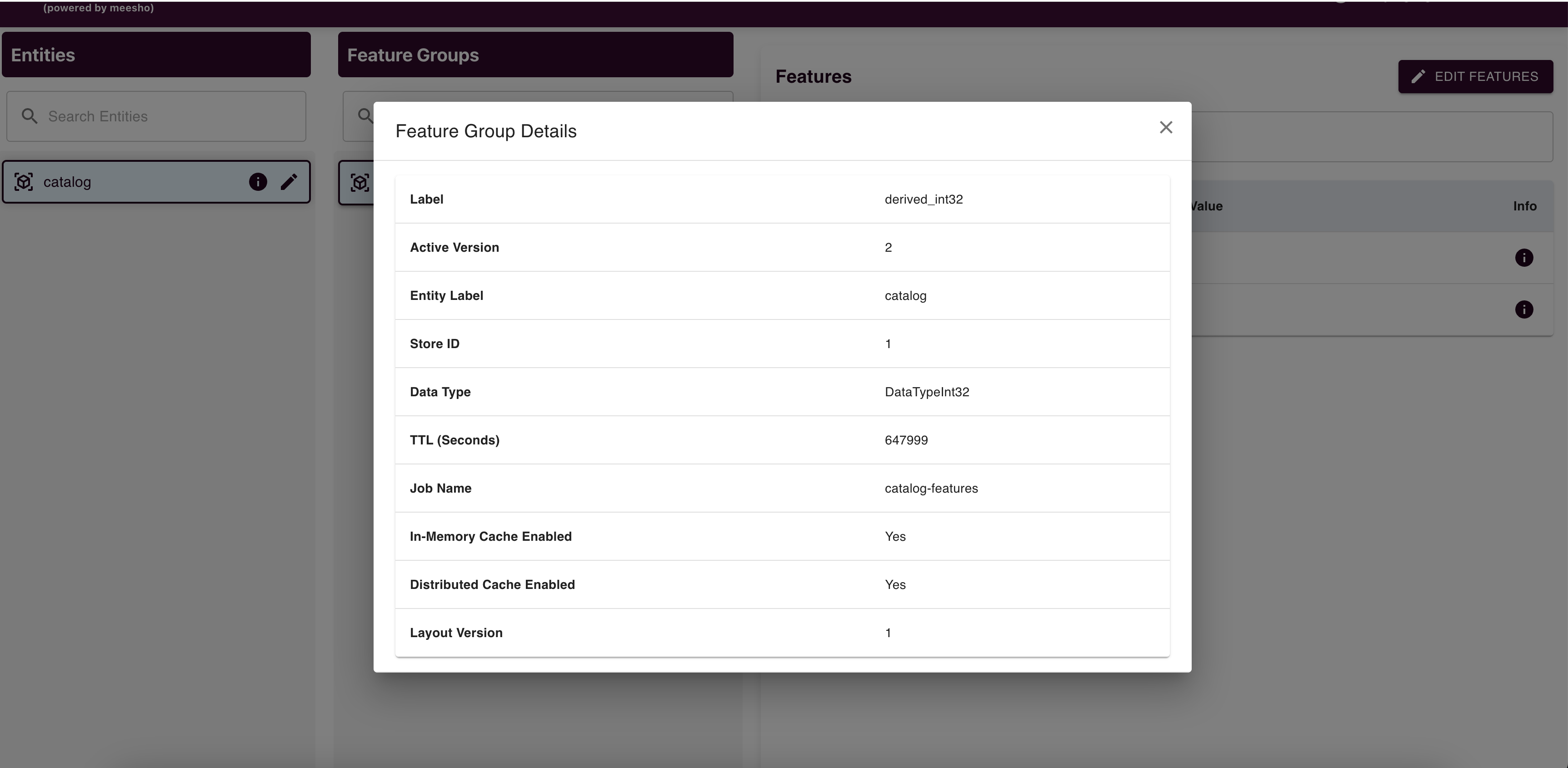
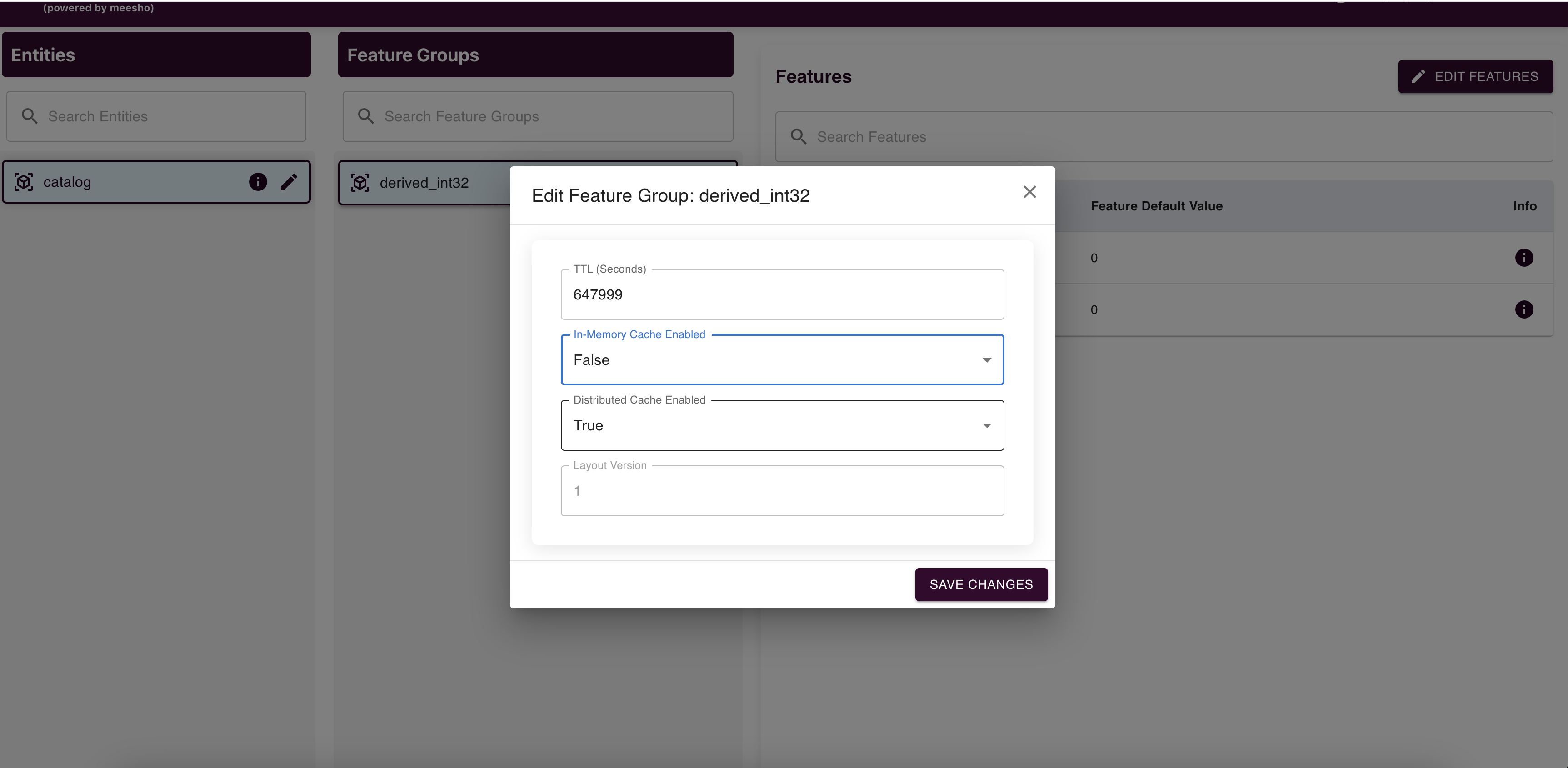
Edit feature groups (TTL, In-Memory Cache Enabled, Distributed Cache Enabled, Layout Version) and submit changes to raise an edit request.
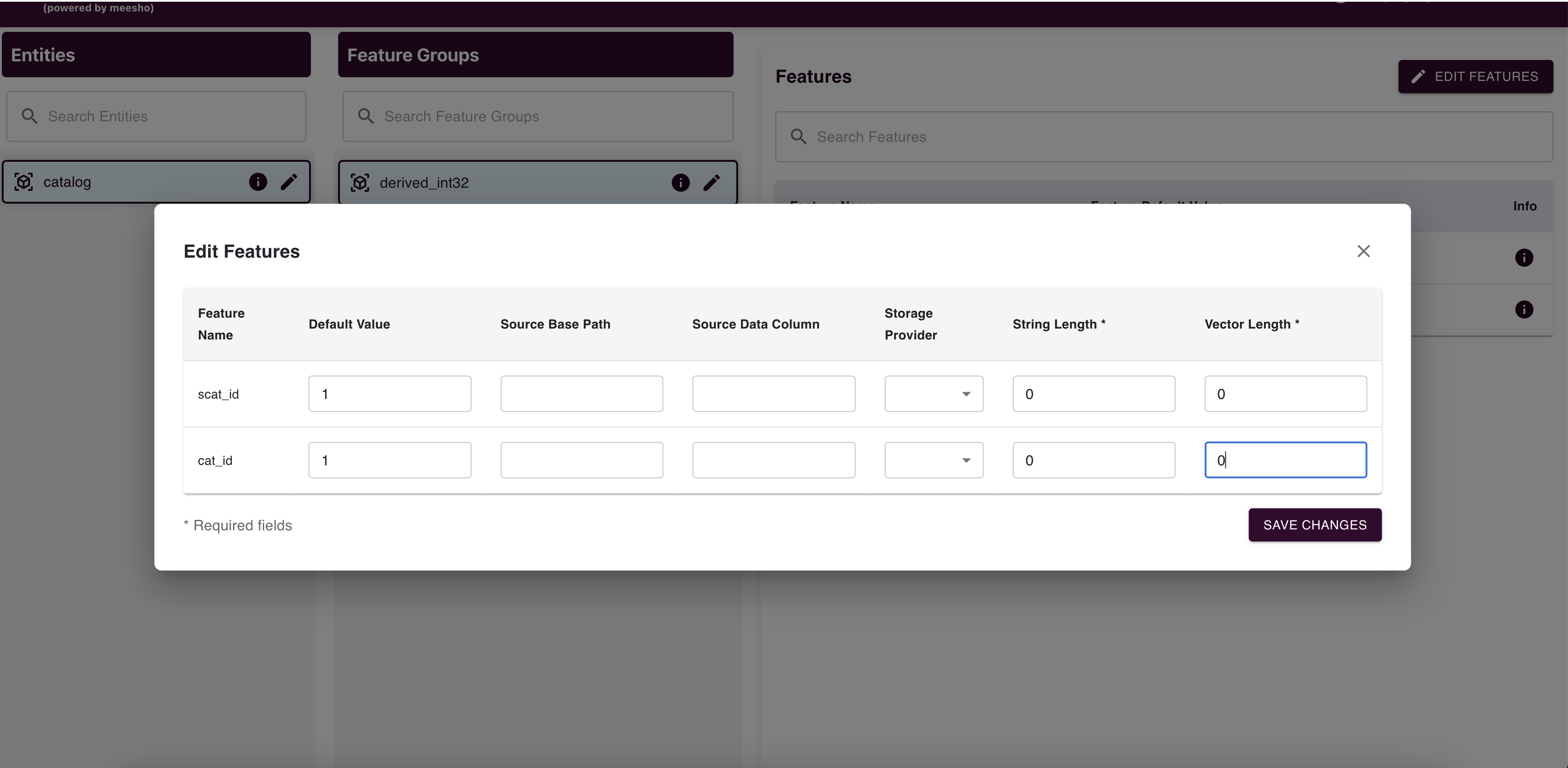
Feature Management
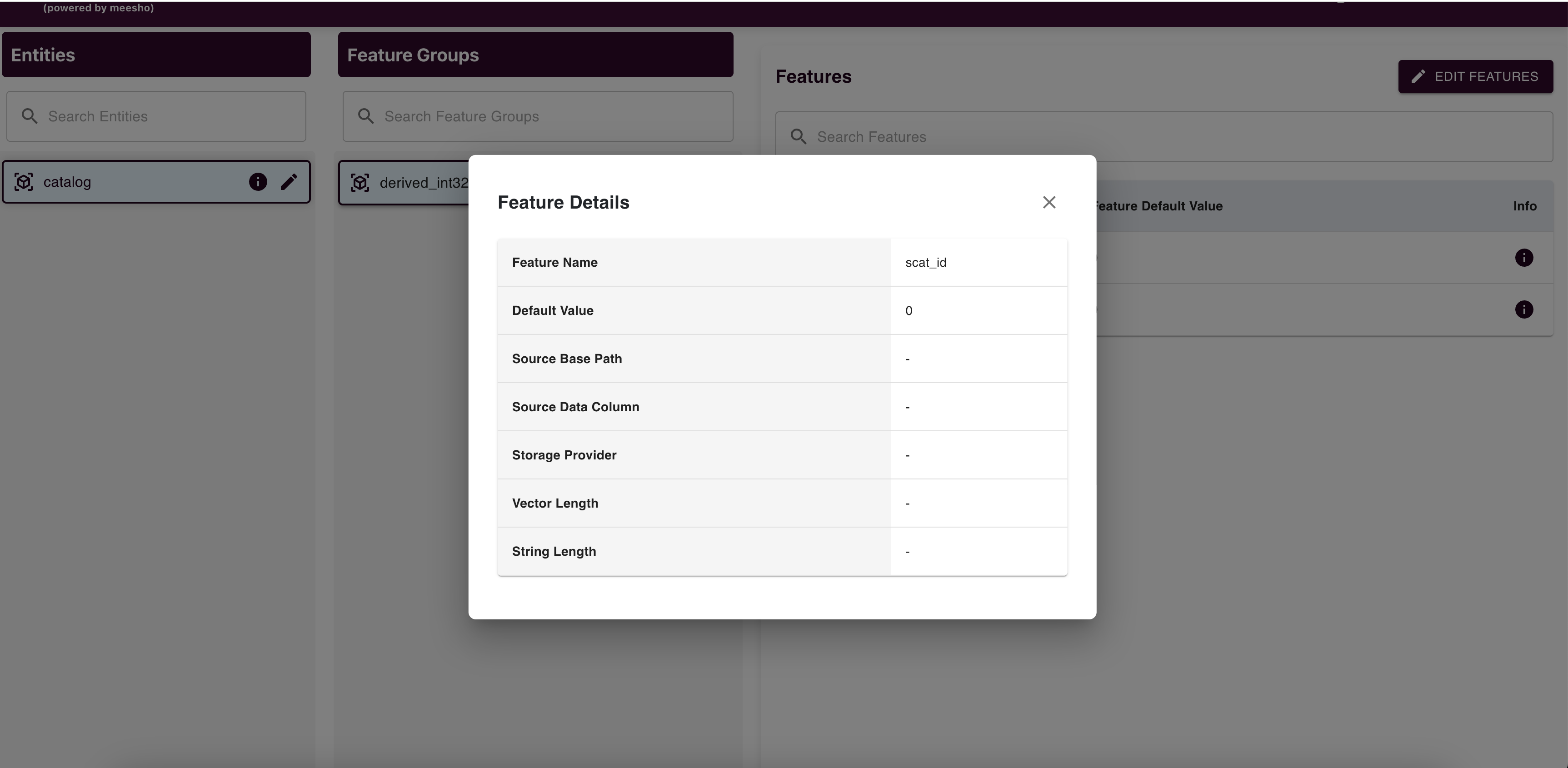
Edit features (Default Value, Source Base Path, Source Data Column, Storage Provider) and submit changes to raise an edit request.
Store Discovery
Access Store Discovery from the Control Center to view all stores in the database.
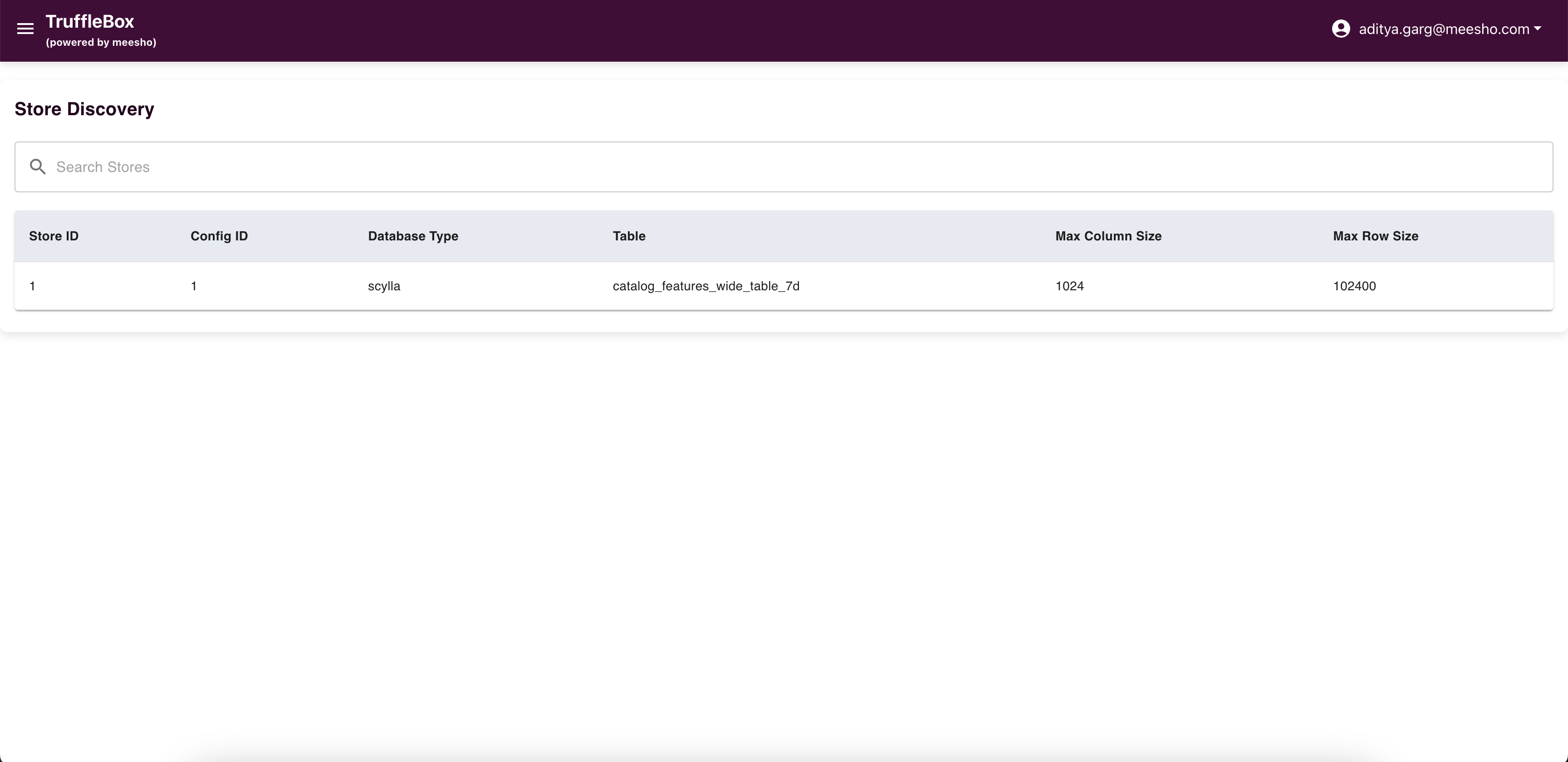
You can search for specific stores but have view-only access.
Job Discovery
Access Job Discovery from the Control Center to view all jobs in the database.
You can search for specific jobs but have view-only access.
Feature Registry
In the Control Center, find the 'Feature Registry' accordion to access various registry options for component registration.

Request Status Tracking
After raising a request, track its status in the respective registry page. For rejected requests, view the rejection reason by clicking the info icon in the Actions column.
Step-by-Step Registration Guide
For proper feature lifecycle management, register components in this order:
- Store
- Job
- Entity
- Feature Group
- Features (if not added during Feature Group registration)
Store Registry
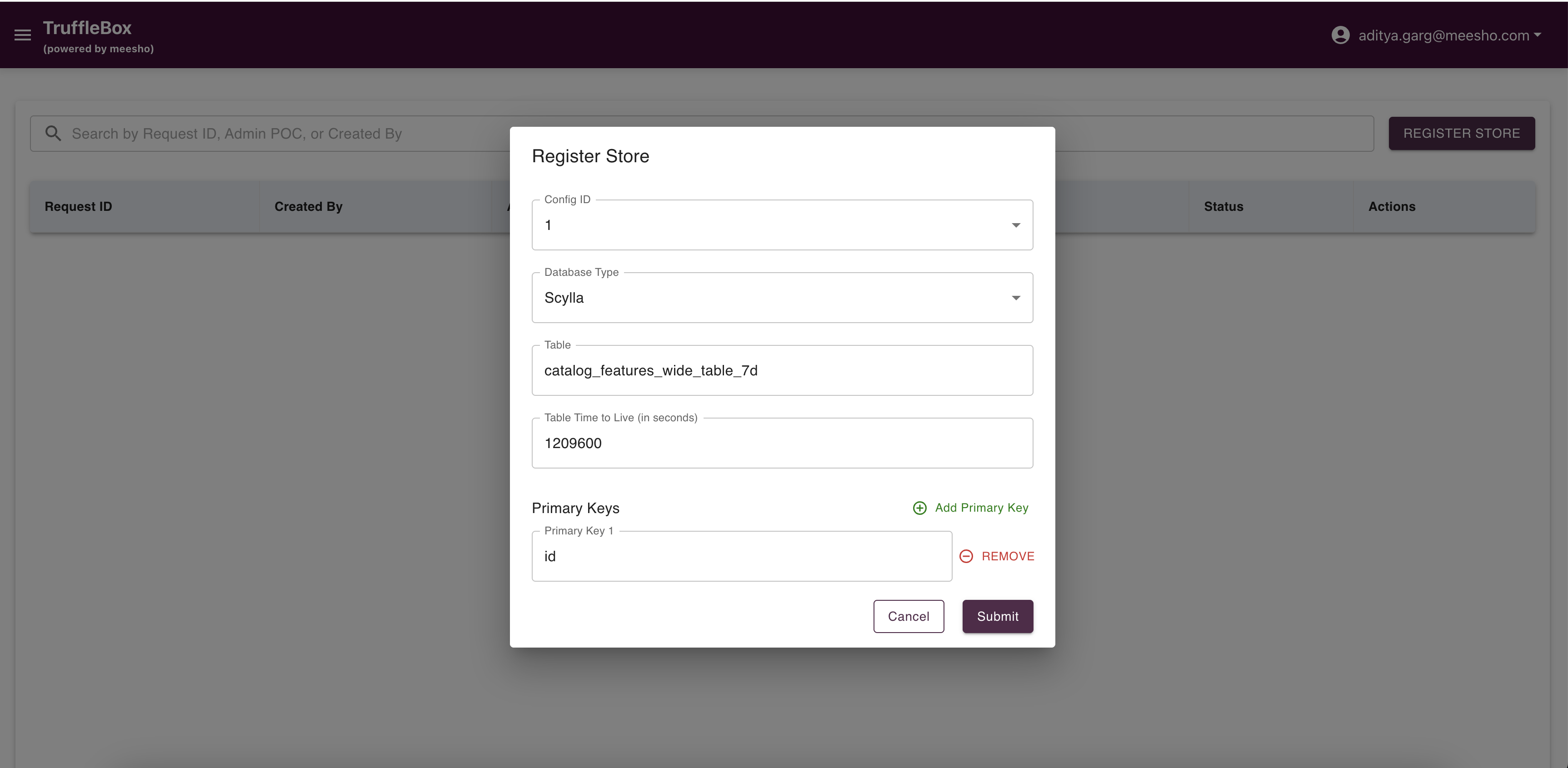
Access Store Registry from the Control Center to view raised requests and register new stores. Fill required data and submit to raise a request.
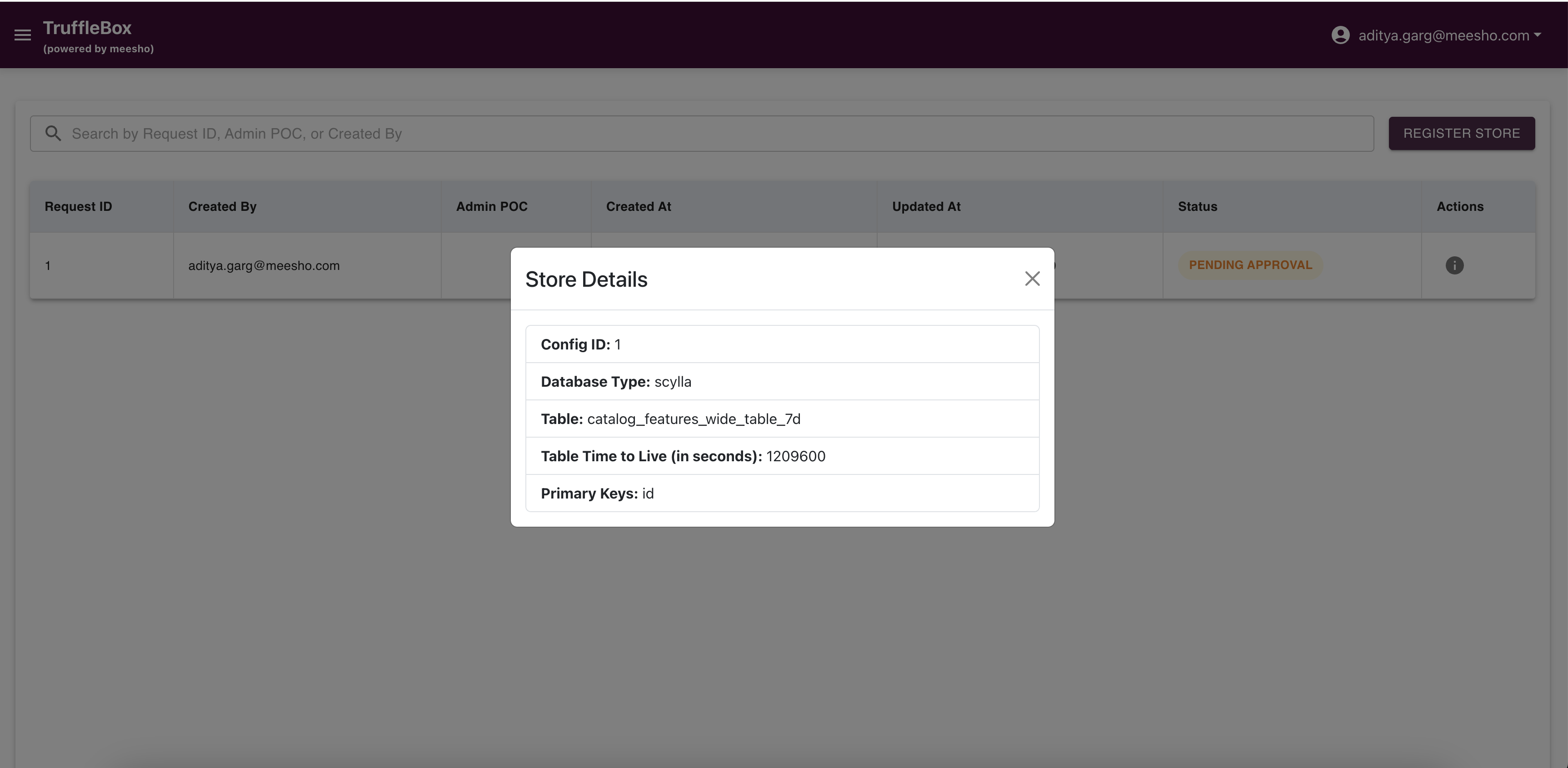
Important Considerations:
- Always add primary keys for proper data identification
- Accurate store configuration is crucial as changes later can be complex
- Admin approval creates a database table with your configuration
Job Registry
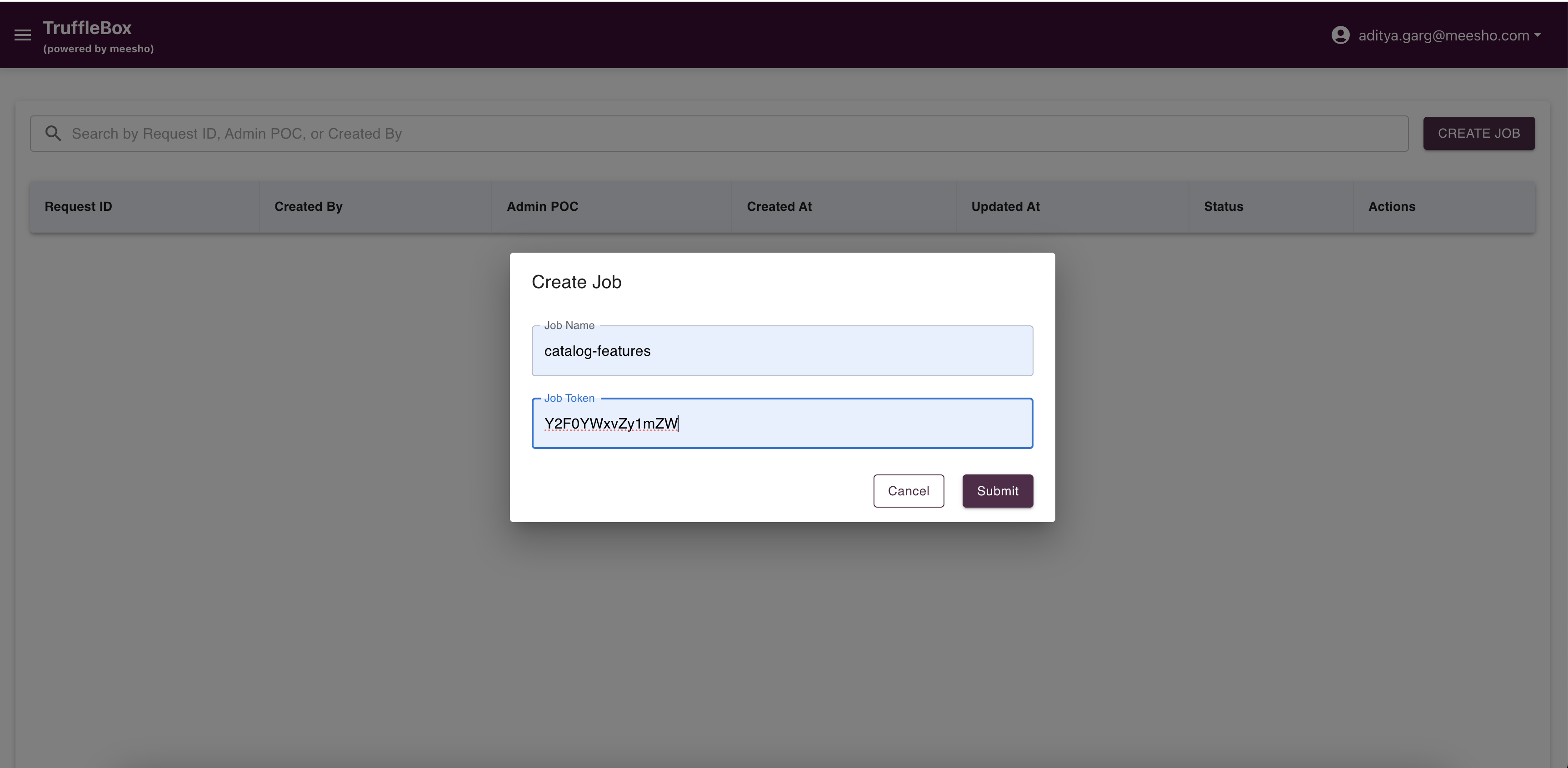
Access Job Registry from the Control Center to view raised requests and create new jobs. Fill required data and submit your request.
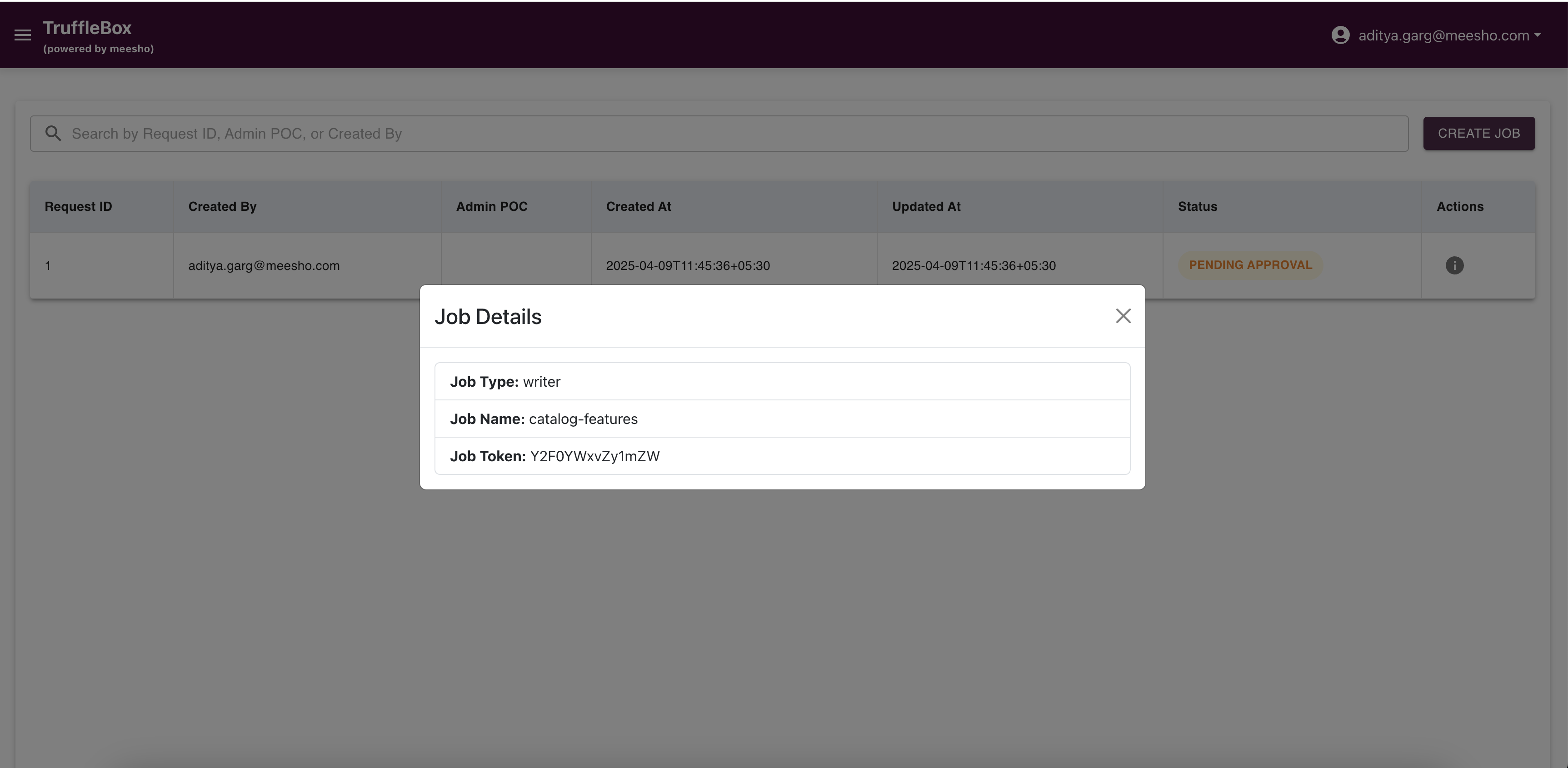
Ensure job details are accurate before proceeding to Entity Registry.
Entity Registry
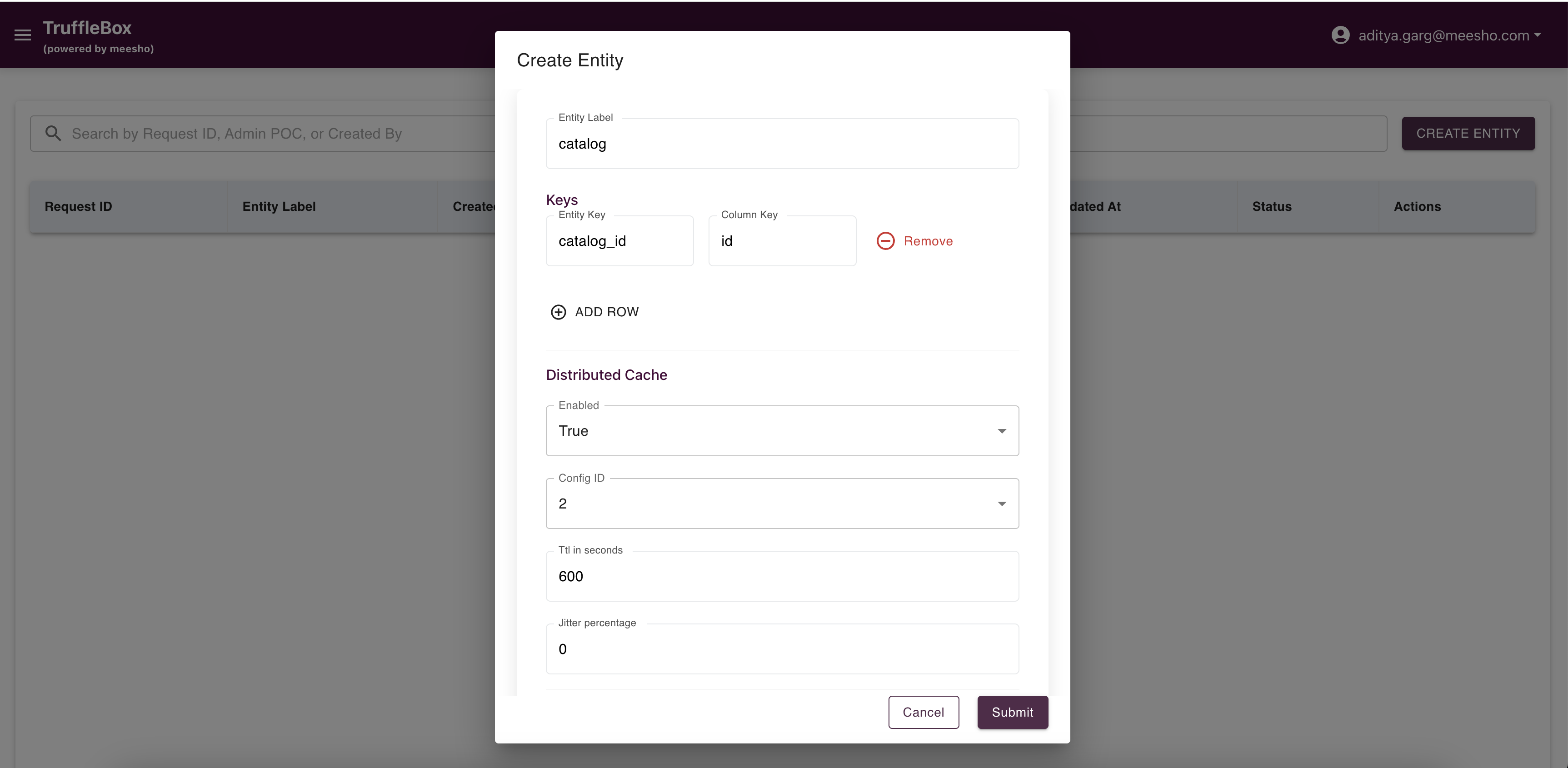
Access Entity Registry from the Control Center to view raised requests and create new entities. Fill required data and submit your request.
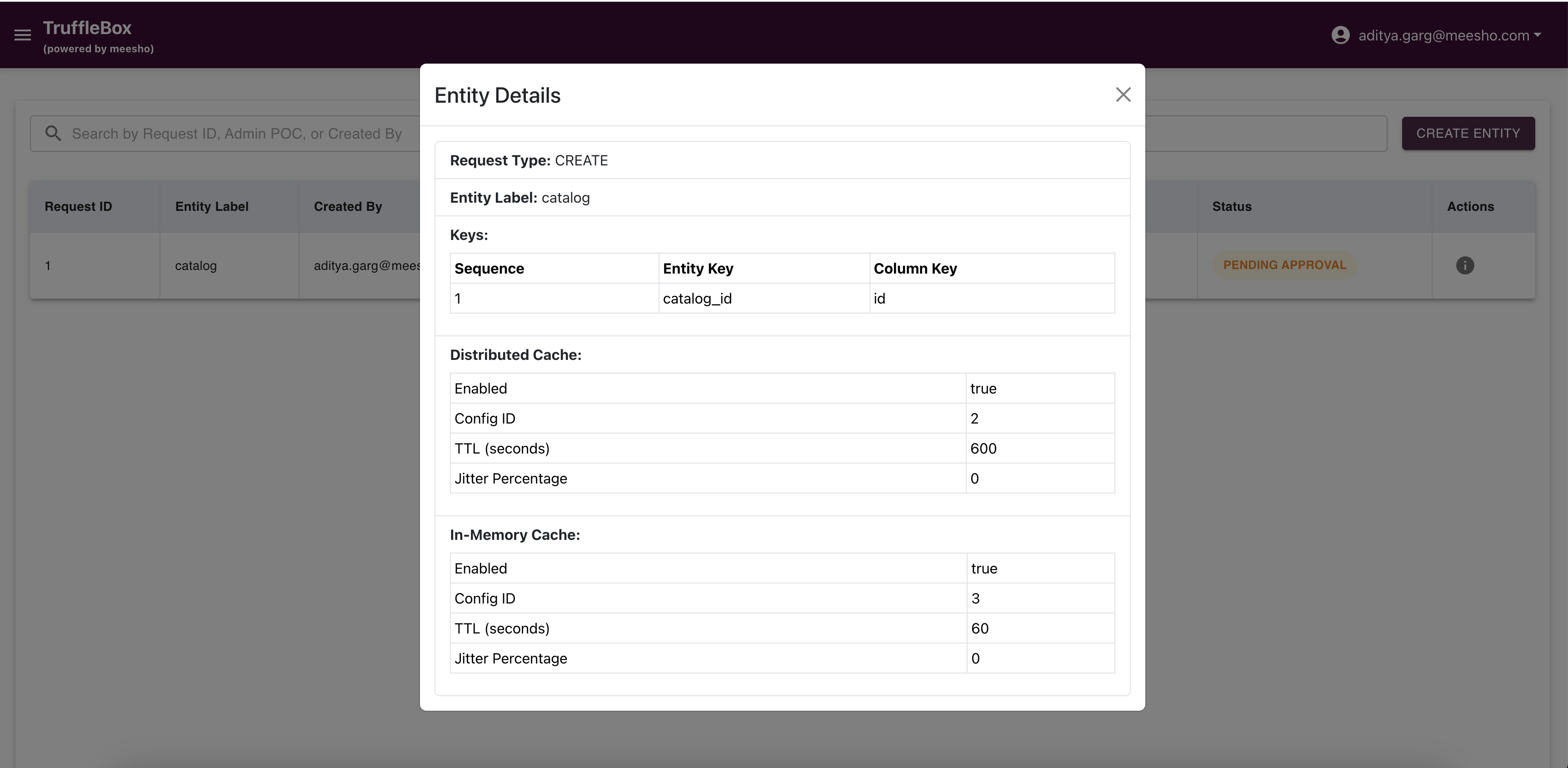
Important Considerations:
- Ensure entity details align with your data model
- The entity serves as a logical container for feature groups
Feature Group Registry
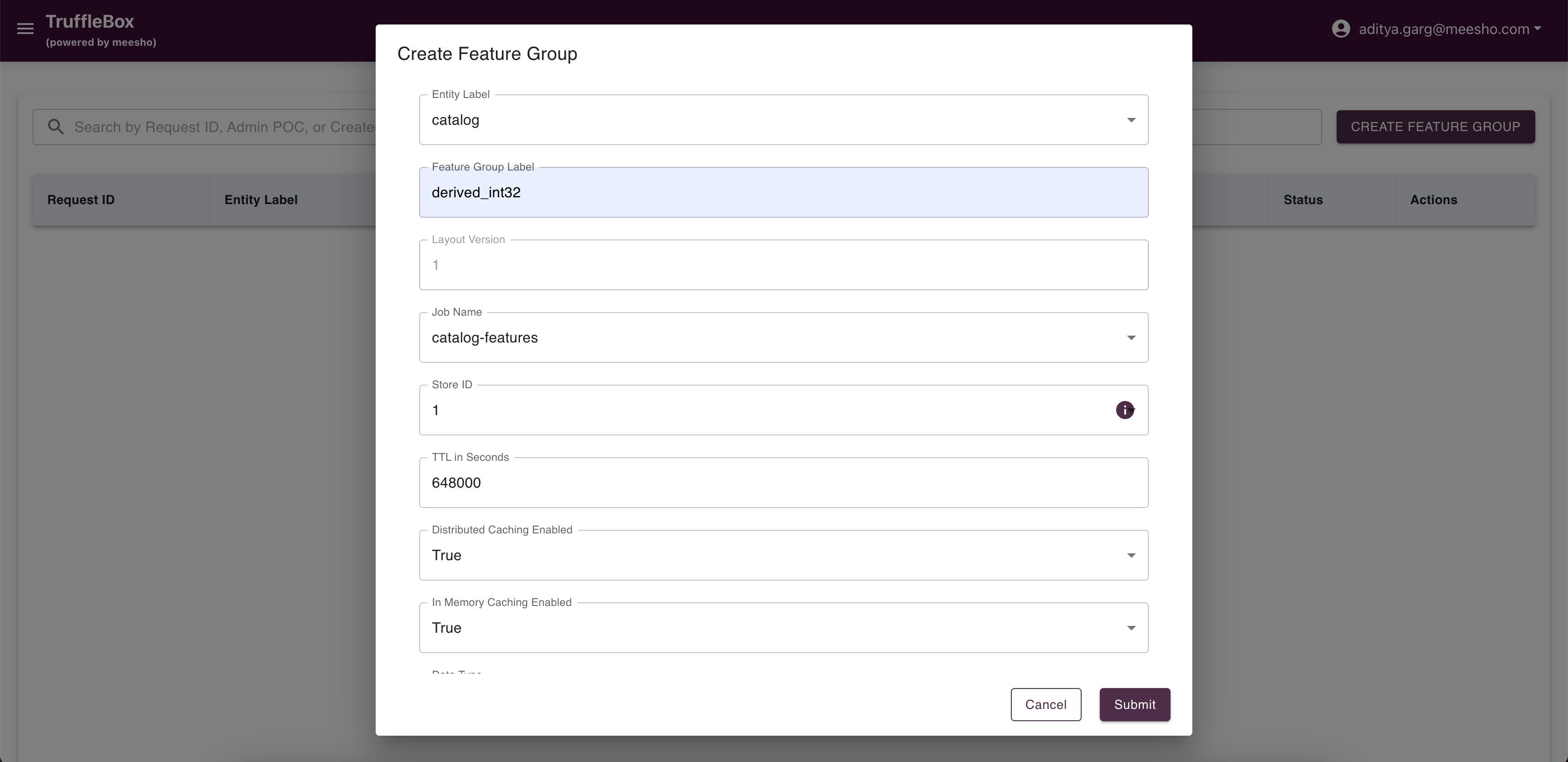
Access Feature Group Registry from the Control Center to view raised requests and create new feature groups. Fill required data and submit your request.
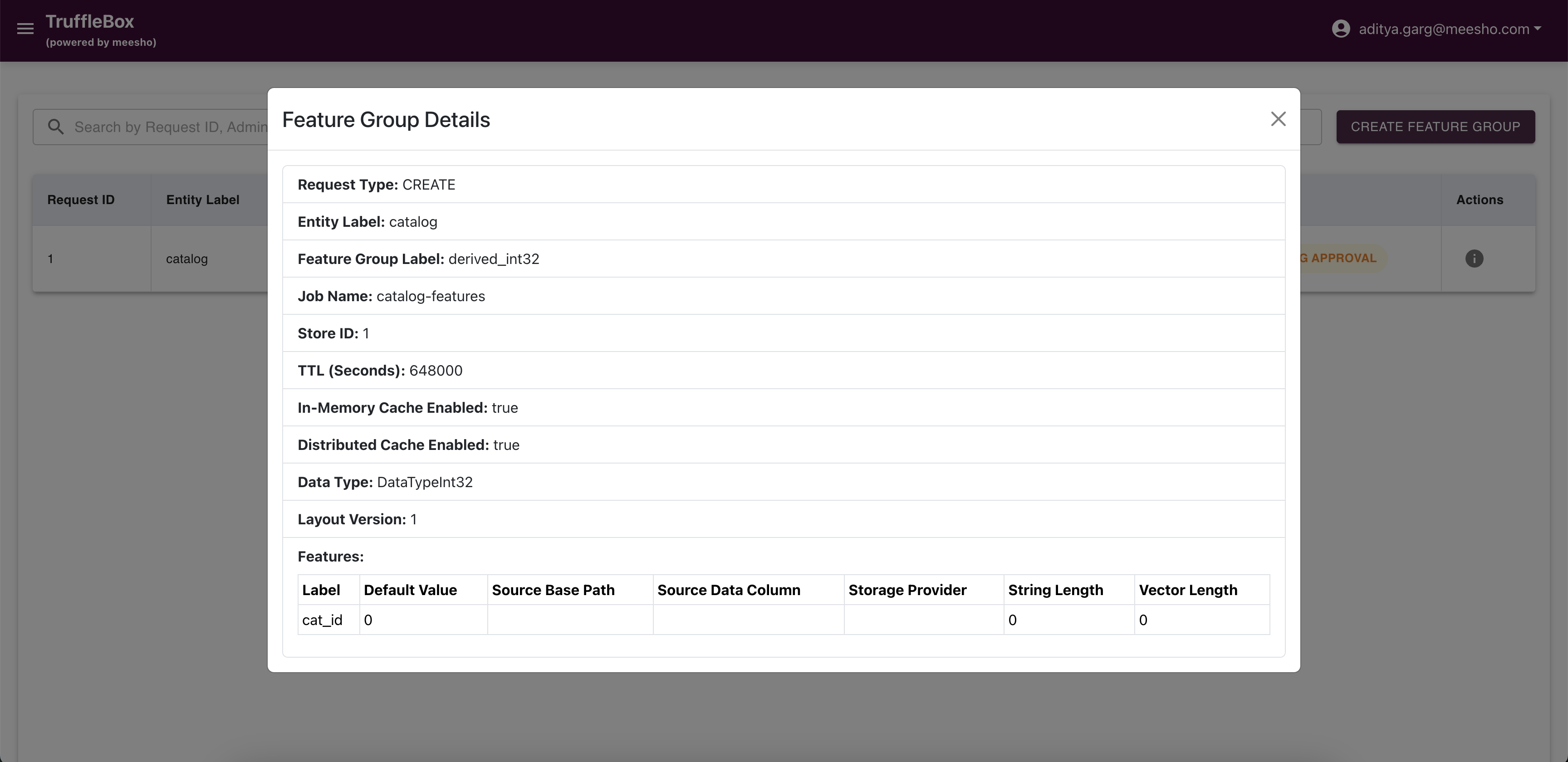
Important Considerations:
- Primary keys must match the store primary keys
- TTL settings determine how long feature data is stored
- Configure cache settings based on access patterns
- Approved feature groups automatically add necessary columns to the database table
Feature Addition
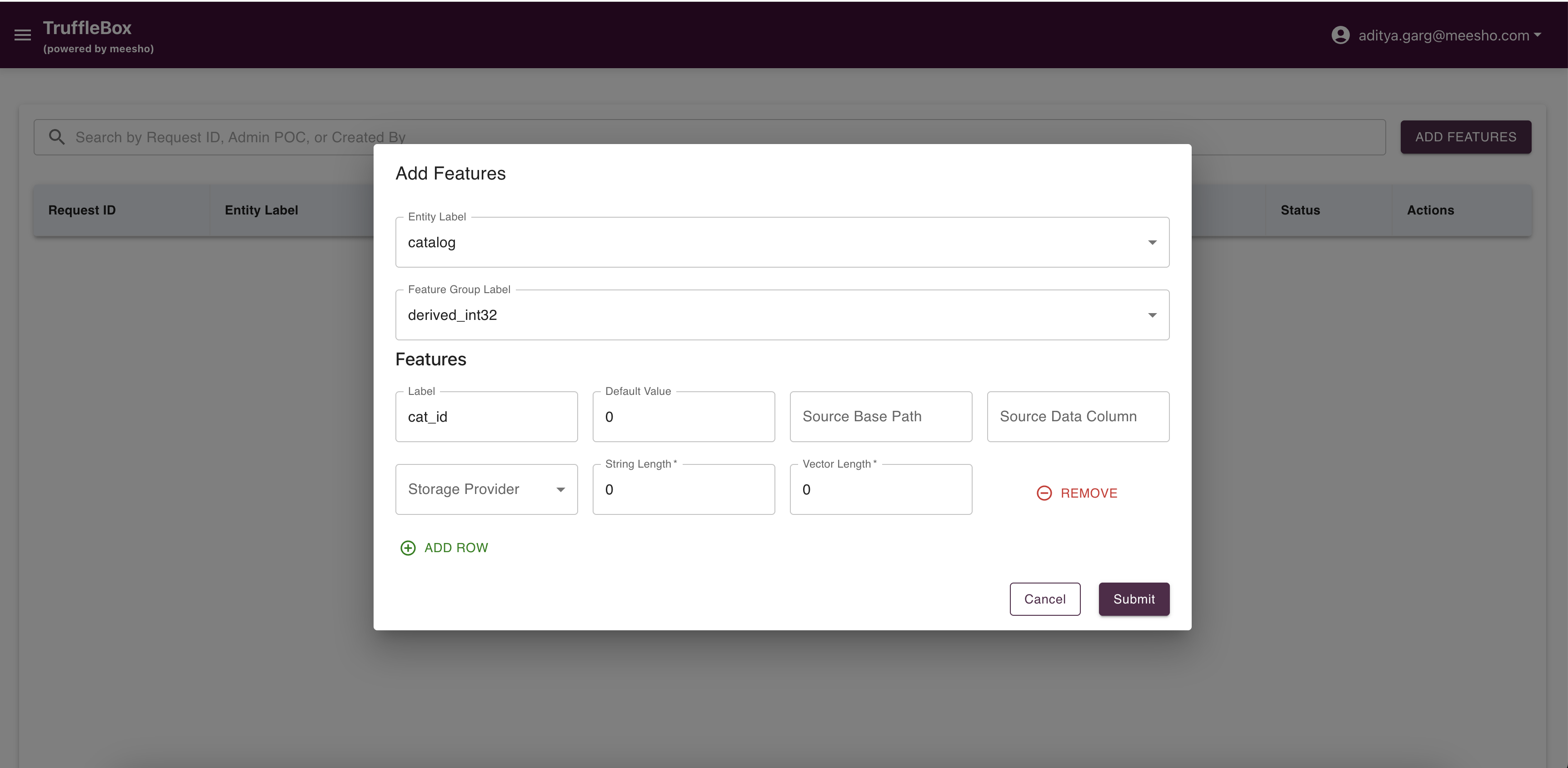
Access Feature Addition from the Control Center to view raised requests and add new features. Fill required data and submit your request.
Important Considerations:
- Ensure feature data types are compatible with source data
- Set appropriate default values and correct source data column mapping
- Approved features automatically add columns to the database table
Need Help?
Please reach out to the BharatMLStack core team for any questions about using TruffleBox.
Admin Approval Flow
As an admin, you're responsible for reviewing and managing user requests.
Request Management
Viewing All Requests
After logging in as an admin, you can see all pending requests across different components (Stores, Jobs, Entities, Feature Groups, Features).
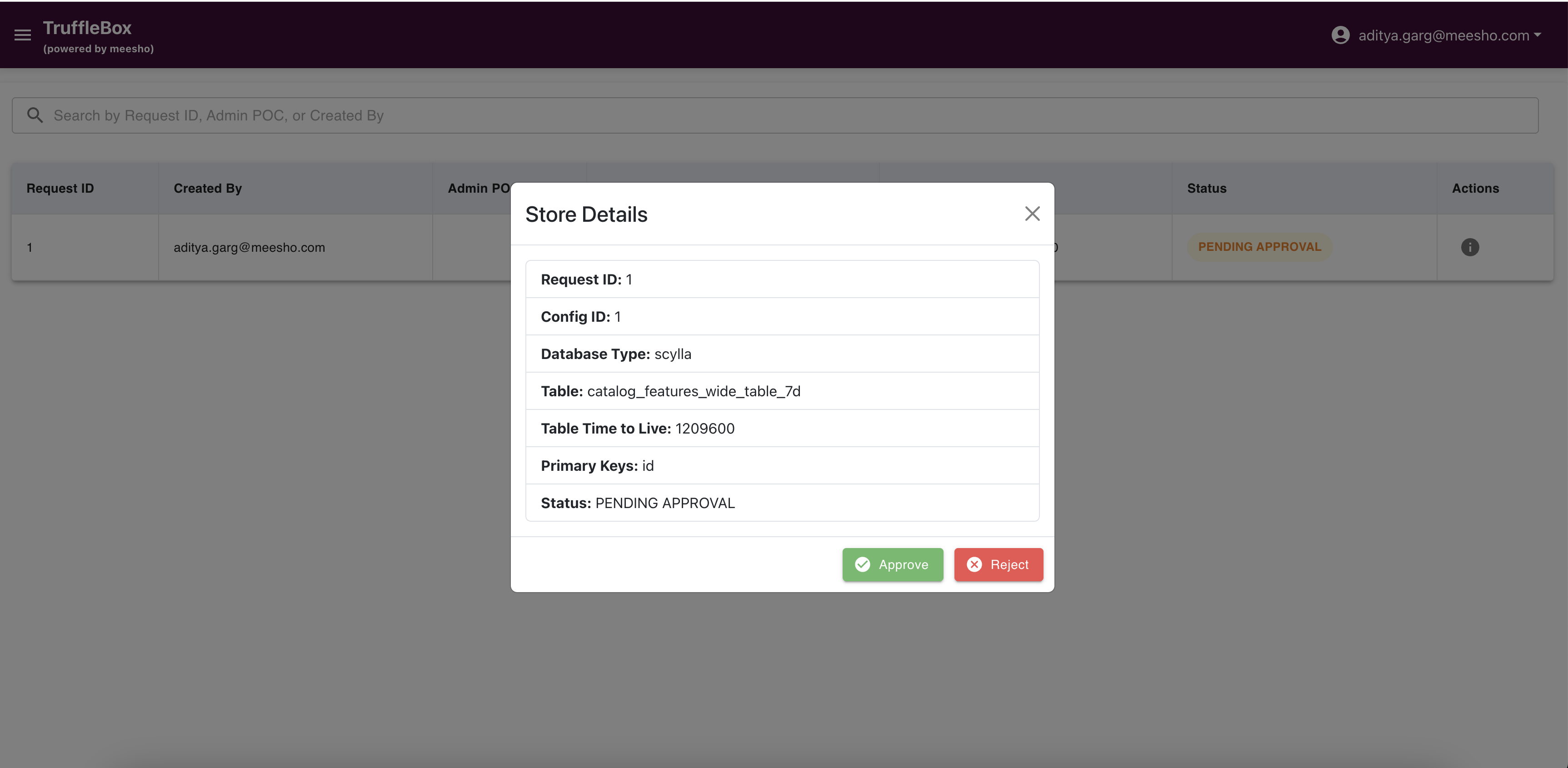
Request Approval Process
- Review Details: Click the info icon to view complete request details

- Approval Option: After review, use the approve/reject buttons

- Approval Process:
Click "Approve" to process the request. The system will create database tables or add columns as needed. A success message confirms completion.

- Rejection Process:
Click "Reject" to deny a request. Provide a rejection reason to help users understand why their request wasn't approved.
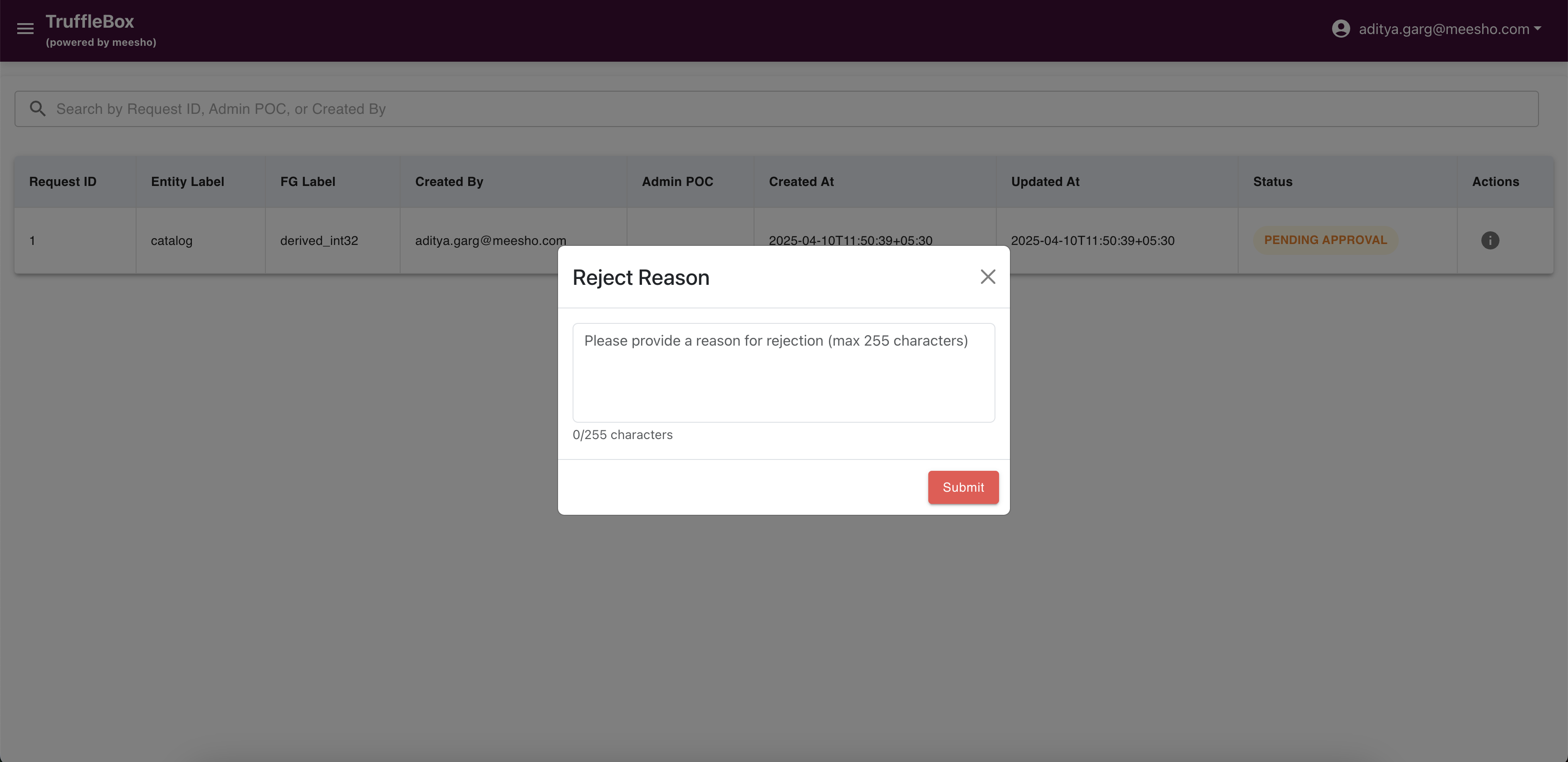
Users can view the rejection reason in their respective registry page.
Admin Support
If you need assistance with admin functions, please contact the BharatMLStack core team.
Contributing
We welcome contributions from the community! Please see our Contributing Guide for details on how to get started.
Community & Support
- 💬 Discord: Join our community chat
- 🐛 Issues: Report bugs and request features on GitHub Issues
- 📧 Email: Contact us at ml-oss@meesho.com
License
BharatMLStack is open-source software licensed under the BharatMLStack Business Source License 1.1.